A
variety of positions are used during physical examination (assessment),
surgical interventions and in nursing patients. These positions are also used
to promote comfort of the patient or to help the patient relax and to prevent
complications.
Common Positions Used
Supine Position
This is where the client lies flat on
the back with legs together but slightly flexed at the knees. The head may be
supported with a pillow.
Uses
It is used to examine the head, face,
neck, limbs, breast, abdomen and the genitalia.
Contra-Indications
This is not used in patients who have
dyspnoea (difficulty in breathing) and also not in patients with burns of the
back.
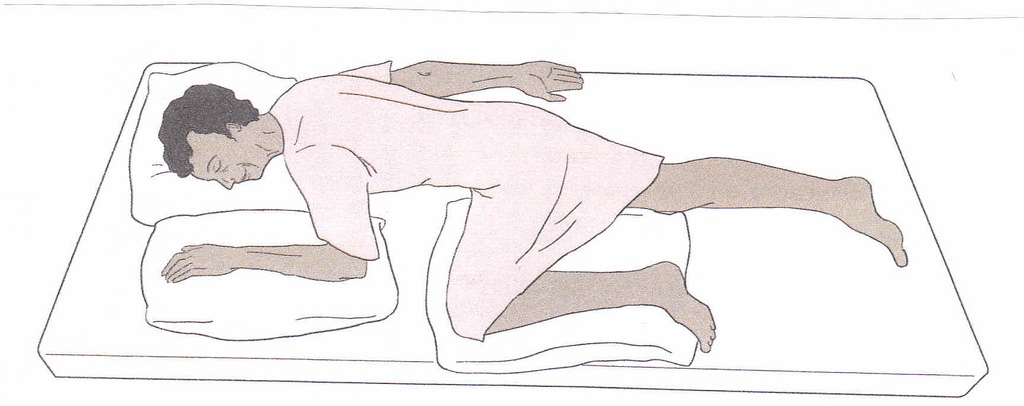
Prone
Position
The client lies on the abdomen, flat on
the bed, with the head turned to one side.
Uses
It is used to assess the hip joint,
posterior thorax, nurse patients with burns at the back, patients with bed
sores and decubitus ulcers on the buttocks.
Contra-Indications
This is not
used after abdominal surgery, respiratory distress and spinal problems.
Fowlers position (Upright)
Patient is
placed in the sitting position and is supported with pillows and back rest.
Client is placed in about 80-90 degrees.
Please note
that Semi - fowlers is when the patient is placed in about 30-40 degrees.
Uses
Patients
with chronic heart disease who have dyspnea, chest and heart surgeries. It is
also used in draining abdominal cavity.
Contra-Indications
This position
is not used in patients who has just had spinal and brain surgery. It cannot be
used in hypotensive clients.
Dorsal Position
Patient lies
on the back with one pillow under the head, legs separated and knee bent with
the sole of the feet on the bed.
Uses
For
abdominal and vaginal examination. Also for patients who have difficulty
maintaining the supine position but needs abdominal examination.
Contra-Indications
Not used in
patients with
burns of the back and fractures of the lower limbs.
Sim’s Position
The patient
lies on either the right or left side and the lower arm behind the body with
the upper arm flexed at the elbow, knees flexed with uppermost leg more acutely
flexed.
Uses
Used in
rectal, vaginal or perineal examination. Also used in giving enema,
suppositories, and then passing of flatus tube.
Contra-Indication
Cannot be used
in client who had just had hip replacement surgery and other orthopedic
surgeries.
Lithotomy Position
With this
position, the patient lies supine with the buttocks at the edge of the
examination table and both legs supported in stirrups.
Uses
Evacuation
or evaluation of the uterus. It is also used in rectal and vaginal examination.
Also used in gynecological examination and in labor ward delivery.
Contra-indication
Should not
be used in clients with joint deformity or strictures.
Trendelenburg’s Position
The patient
lies in supine position with the head side of the bed brought 30-40 degrees lower than the feet.
Uses
It is used
in treating shock, hypotension and in pelvic examination.
Contra-Indication
Should not be
used in head injuries, spinal injuries, unconscious patient etc.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/supine_position-5bb0ec5146e0fb002693dccc.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/prone_position-5bb0ece34cedfd0026f7b558.jpg)




Comments
Post a Comment