Scroll down to proceed with verification👇🏾
Featured post
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Family Planning; Know the available contraception
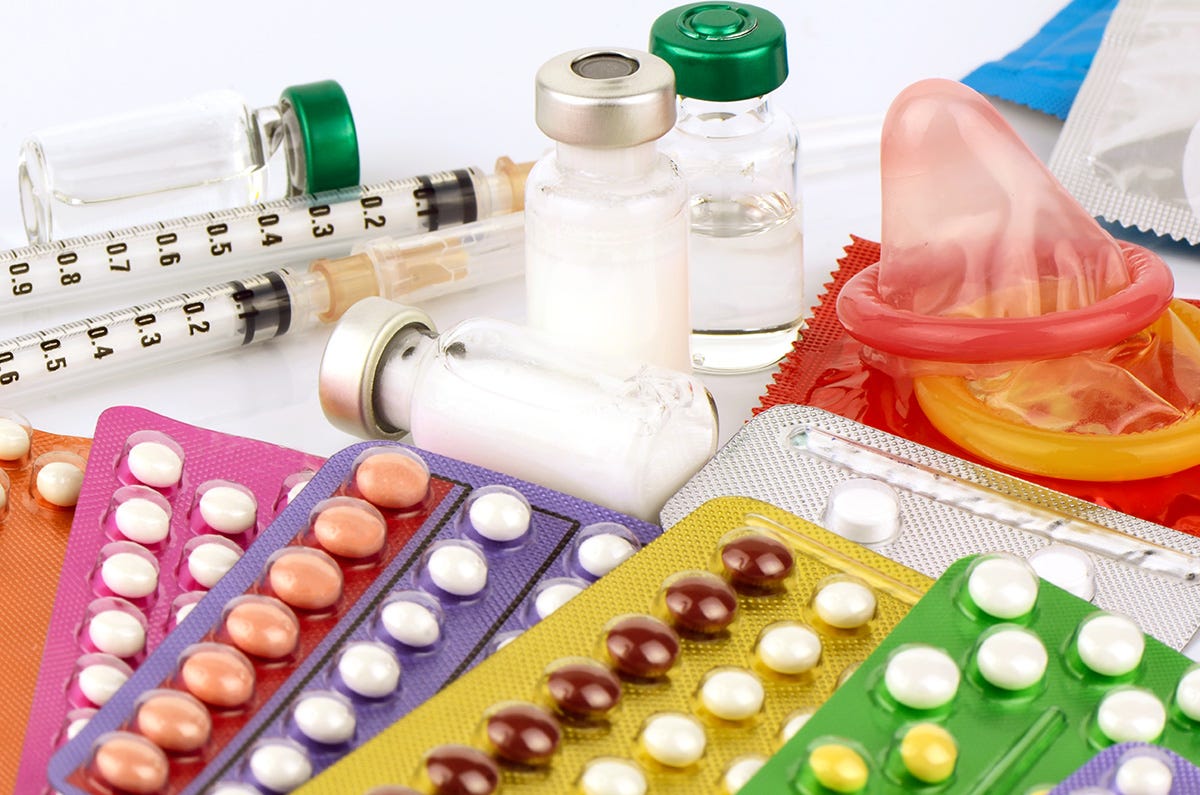
Introduction
Is the ability of a couple to decide the number of children to have, when to have them and by using a particular contraceptive method. Contraception is the use of temporary techniques to prevent pregnancy while allowing intercourse to continue.
The ideal contraceptive should be safe, harmless and not interfere with the sexual enjoyment of either party. Contraception is an important factor in many women's lives, with needs varying according to the particular stage of the life continuum, and should also be viewed in the wider context of sexual and reproductive health. The capacity to enjoy and control sexual and reproductive health behaviors is a key element of sexual health (WHO 1992).
Yet this is not the experience of many women. Unintended pregnancies can have long-lasting effects on the quality of life of parents and children. Family planning is a personal matter demanding a low failure rate. It is worth noting that most family planning methods does not provide 100% guarantee against pregnancy. Some of these methods can be combined with other.
The failure rate of any method of contraception is judged by the Pearl index (PI): the number of women having regular intercourse who become pregnant within a year out of 100 couples using the method. The uses of family planning methods have been influence by a lot of factors in the society, which includes;
- Age
- Partners concern, for example, Religion.
- Culture.
- Scarcity.
- Insufficient advertisement of contraceptives.
- Personal health.
- Personal habits.
Reason for practicing family planning
- It reduces maternal mortality and morbidity.
- It reduces neonatal mortality and morbidity.
- It helps mothers to rest in between pregnancy and gain strength before another one.
- It improves standard of living.
- It also gives parents an opportunity to prepare for the arrival of each child.
- It prevent illegal abortion that may lead to death.
- It corrects some menstrual disorders in women.
- It help to prevent over population.
- If it can prevent over population, then we can also say it helps to reduce burden on government expenditure.
Family planning methods
We will be discussing the methods of family planning under these topics;
- Short term methods
- Long term methods
- Barrier methods
- Natural methods
- Permanent methods
- Emergency contraceptives methods
Short term methods
These are family planning methods which are used for a short duration (from days to months). They include: creams, foams, jellies, oral pills, injectable, douching, contraceptive patch, vaginal ring etc.
Oral contraceptive pills
Out of the different family planning methods, this is the most common and popular artificial method of family planning. The oral pill restricts the development of the egg and increases the thickness of the cervical muscles stopping the sperm from reaching the egg. If the regular course of birth control pills fails, then emergency pills can be taken during unsafe sex to minimize the chance of pregnancy. For example Loestrin 20, Loestrin 30, Brevinor, Norimin .Microgynon 30, secure, Levon 2 etc.
 |
| Photo by News Medical |
Advantages
- The pill is the most effective method of reversible birth control provided the instructions are followed and it is taken regularly.
- The method is not related to the act of intercourse.
- Women who suffer from dysmenorrhoea or heavy periods often find their periods less painful and the flow diminished.
- Menstruation occurs at regular intervals of four weeks.
- Haemoglobin levels are maintained so that anaemia is less common.
- It is not cost efficient (not costly).
- It prevent pelvic inflammation disease (PID).
- It may reduce acne and hirsutism.
Disadvantage
- It increase vagina discharges
- It could alter menstrual period or cause irregular menstrual period.
- No protection against STIs.
- Needs regular supply.
- It has to be taken daily for maximum effectiveness.
Contraindications of Oral Contraceptives.
- Breast-feeding mothers and less than 6 weeks postpartum.
- Age =35 years and smoking about 15 cigarettes per day
- Multiple risk factors for arterial cardiovascular disease (e.g. older age, smoking, diabetes, hypertension etc.)
- Elevated blood pressure of 160 mmHg systolic or 100 mmHg diastolic and above.
- Current or history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
- Major surgery with prolonged immobilization.
- Current or history of ischemic heart disease and complicated valvular heart disease.
- Stroke
- Migraine with focal neurologic symptoms (migraine with aura).
- A woman with migraine without focal neurologic symptoms whose age is greater than or equal to 35 years.
- Current breast cancer.
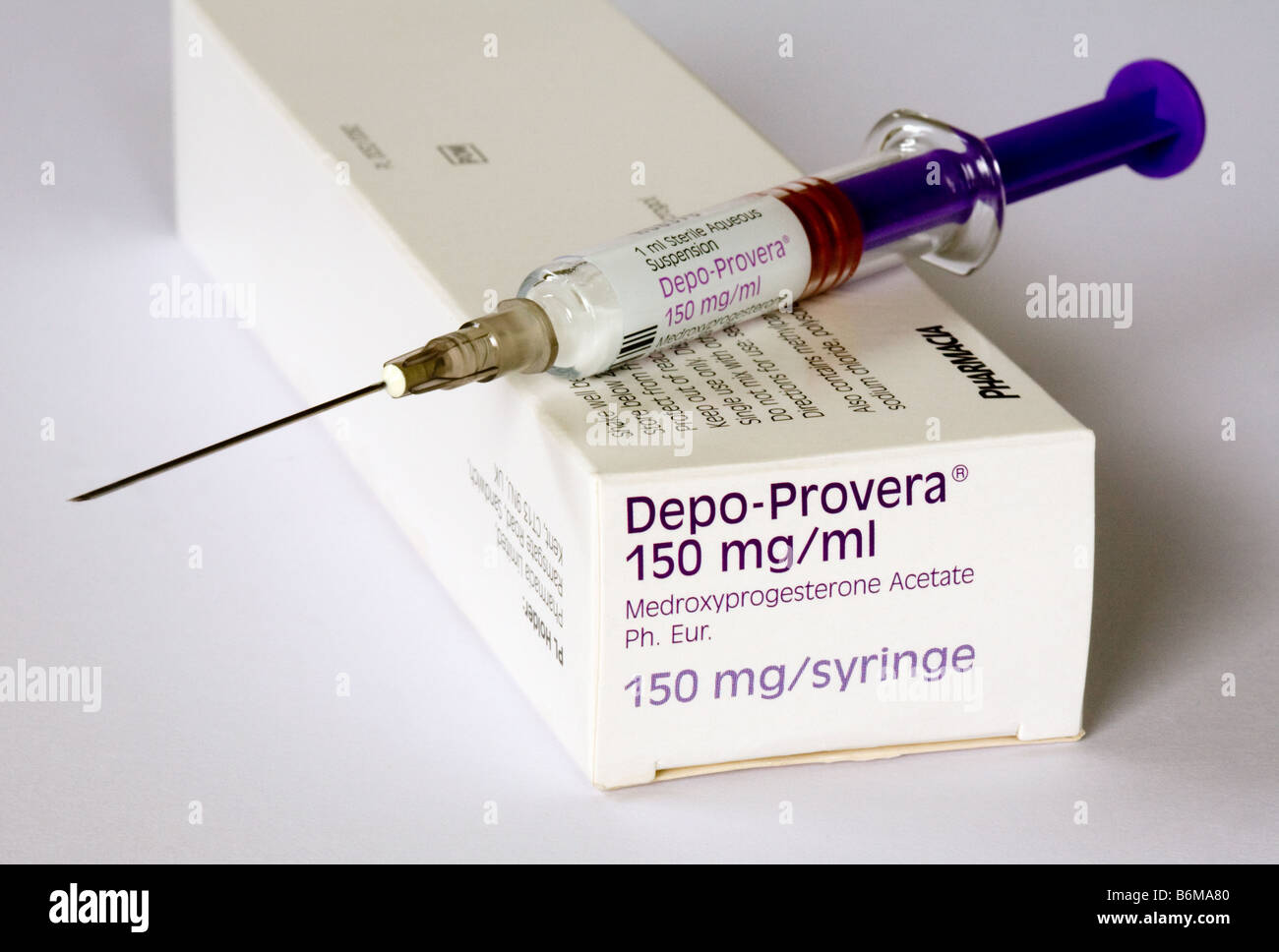
Injectable Contraceptives
Those most commonly used consist of a progestogen given usually by intramuscular injection. The injectable, containing 150 mg of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate, inhibits ovulation, produces an atrophic endometrium, and alters cervical mucus to decrease sperm penetration.
Intramuscular injections are administered every 3 months (within a window of 2 weeks on either side). This injectable contains 25 mg depot medroxyprogesterone acetate and 5 mg estradiol cypionate. Examples of injectable contraceptive are Depo-medroxy-progesterone acetate (Depo-Provera) which is given in a dose of 150 mg repeatedly every 12 weeks or 90 days. Norethistdrone enanthate (Noristerat) is given every two months.
Advantages
- It prevents anaemia
- It help to prevent ectopic pregnancy.
- It prevent endometrial cancer.
- Ability to combine with other methods, the effectiveness increases when this happens.
- It increase sexual enjoyment because there is no need to worry about pregnancy
Disadvantages
- Some women report weight gain, headache and nausea.
- Many women experience irregular and prolonged bleeding.
- Requires an injection every one, two or three months. (the pain and discomfort).
- A woman cannot get pregnant immediately after discontinuation.
Long term method
These are family planning methods which are used for a longer duration, that is, for several years until the individual is in need of a baby. Examples of long term methods are:
Intrauterine device (IUD)
Intrauterine devices have existed for centuries. In the past, devices were made of plastic, one of the better known being the Lippes loop, which is rarely seen in the Western world now.
It is a small device made of metal, plastic or copper that is inserted in the uterus of a woman who does not plan an increase in her family for some time. It prevents fertilization by restricting the sperm from entering the uterus, and thus prevents pregnancy for five to ten years. This device should be used under the guidance of a medical practitioner only.
Advantages
- Can be inserted immediately after childbirth.
- It gives permanent protection and requires no attention at the time of intercourse.
- Provided that there are no complications, a device can remain in the uterus for up to five to ten years.
- Leads to less risk of ectopic pregnancies compared to woman who do not use any contraceptive method.
- Has no interaction with any medicine
- It is about 95-99% effective
Disadvantages
- It can be expelled unknowingly by the wearer (get out of place)
- It produced excessive menstrual bleeding.
- It give uterine cramps.
- No protection against STIs/AIDS.
- Professional skill needed to initiate and discontinue use.
Contraindications of IUD includes;
- Pregnancy.
- Puerperal sepsis.Immediate post septic abortion
- Anatomic abnormalities that distort the uterine cavity.
- Unexplained bleeding, suspicious for a serious condition.
- Malignant gestational trophoblastic disease.
- Cervical cancer.
- Breast cancer (for progestogen-releasing lUDs only).
- Endometrial cancer.
- Uterine fibroids with distortion of the uterine cavity.
- P1D—current or within the last 3 months.
- Sexually transmitted infections—current or within the last 3 months.
- Known pelvic tuberculosis.
Norplant (Jedal)
Silastic capsules injected subcutaneously under local anaesthesia. Levonorgestrel implants (Norplant) offer up to five years of protection and can be removed when the return of fertility is required. Alternatively, at five years they can be replaced.
 |
| Photo by Science Photo Library |
Advantages
- It is safe and effective (99%).
- Can last for five (5) years.
- Increase sexual satisfaction.
- Prevent endometrial cancer.
Disadvantages
- Not easily removable.
- Required professional skills for insertion and removal.
- No protection against STIs/AIDS.
- Irregular bleeding.
- Amenorrhea.
- Skin reactions.
Barrier methods
These are family planning methods which prevent the male sperm from reaching the cervix or coming into contact with the vagina. They includes; condom, cervical cap, diaphragm, spongy, Vault pessary, Vaginal sheath etc.
Spermicidal contraceptives are use with some of the barrier contraceptive. They make the sperms inactive before they enter the uterus in any case.
Male Condom & Female condom
 |
| Photo by spy.com |
The sheath, condom or French letter is one of the commonest methods of contraception. It requires no medical intervention and can be bought in many non-medical places. For maximum safety the woman should insert a chemical contraceptive in case the sheath bursts or slips off.
Advantages
- It is cost effective (cheap to buy).
- It doesn’t need examination by doctors.
- It provide protection against STD.
- It is disposable.
Disadvantages
- Cannot be used if allergic to rubber.
- Can cause irritation.
- They decreased sexual pleasure.
- The condom can slip off or burst (tear/break) during the process of sexual intercourse.
Instructions
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides the following instructions for correct use of male condoms:
- Use a new condom with each act of sexual intercourse.
- Handle the condom carefully to avoid damaging it with fingernails, teeth, or other sharp objects.
- Put the condom on after the penis is erect and before any genital contact with the partner.
- Ensure that no air is trapped in the tip of the condom.
- Ensure adequate lubrication during intercourse, possibly requiring the use of exogenous lubricants.
- Use only water-based lubricants with latex condoms (oil-based lubricants can weaken latex).
- Hold the condom firmly against the base of the penis during withdrawal, and, to prevent slippage, withdraw while the penis is still erect.
Natural methods
This is a method of family planning which does not require any contraceptive. They include: lactational amenorrhea, coitus interruptus, calendar method, cervical mucus method, basal body temperature method etc.
Lactational Amenorrhea
Lactation can be considered as a method of family planning when used properly. It provides about 98% protection against pregnancy during the first 6 months following delivery if the mother is still amenorrhoeic and fully breastfeeding her infant. LAM is very effective method if the following three criteria are met:
- The woman is amenorrhoeic.
- The woman is fully breastfeeding (does not give the infant supplementary food).
- The baby is less than six month old.
Advantages
- It can be use immediately after birth.
- No direct cost for family planning.
- No supplies or procedure needed to prevent pregnancy.
- No hormonal side effect.
- It encourages exclusive breastfeeding.
Disadvantages
- It is only done by breastfeeding mothers.
- The duration is relatively limited.
- It does not protect the woman against STI/HIV.
Withdrawal/Coitus interruptus
This is the oldest and a widely practiced method; the male withdraws before ejaculation. It is not always reliable because human beings are frail.
Advantages
- It is easy.
- It helps to prevent unwanted pregnancy.
- It involves no cost to practice.
- Require no consultation.
Disadvantages
- It does not protect against STI/HIV.
- It needs strong commitment.
- It is not 100% effective.
- It lead to unwanted pregnancies.
The calendar method
This method is based on working out the fertile period from previous cycles. Calendar-based methods require abstaining from unprotected intercourse during the woman’s fertile period, which is estimated from the typical length of her menstrual cycle and from assumptions about the timing of ovulation, how long the ovum is capable of being fertilized, and the length of time sperm can survive in the female genital tract.
One method estimates the fertile period to be from the length of the shortest cycle minus 18 to the length of the longest cycle minus 11. For example, if the woman's shortest cycle was 25 days and her longest cycle was 29 days, her fertile period (i.e., when abstinence is required) would be from day 7 through day 18.
Another version, the standard days method, simply states that for women whose cycle lengths are between 26 and 32 days, the fertile period is from days 8 through 19 of their cycle.
The basal temperature method
It is dependent on the rise of basal temperature which follows ovulation. The basal body temperature method is based on temperature changes throughout the menstrual cycle. A rise of 0.4 to 0.8 degrees above the mean (average) temperature of the preovulatory phase for 3 days indicates ovulation has occurred. Therefore, abstinence is required from the time of menses until 3 days after the rise in temperature.
The cervical mucus method
This method entails checking the quality and quantity of cervical mucus each day; the fertile period is indicated by clear, wet, and slippery mucus. Abstinence from unprotected Intercourse is necessary during menses, every other day during the preovulatory period (as intercourse interferes with interpreting the cervical mucus signs), and from the time fertile mucus appears through 3 days after the last day of fertile mucus.
Advantages
- It is easy to practice.
- No cost is involves.
- No hormonal side effects.
- If practiced properly or with other natural methods, it is effective.
Disadvantages
- It does not provide protection against STIs/HIV.
- The practitioner needs to be educated before one can use it.
3 Illiterate women cannot use some of the methods e, g. calendar method.
4 Women who fear to insect their fingers in to their vagina cannot use the cervical mucus method.
Permanent method
These are family planning methods practices by a couple (or individual) who do not need children any more. They are; vasectomy and female sterilization.
Counseling for sterilization
Sterilization is an important step in the life of any man or woman, it should be considered as irrevocable for, while reversal is possible for both males and females, success cannot be guaranteed even in the most expert hands.
Counseling is important and consent must be given in writing. The consent of the spouse is no longer necessary legally, but it is desirable that the couple should be seen together and the full implications of the procedure explained. A girl under 16 cannot consent to sterilization, nor can her parents insist on it. The same applies to individuals who are mentally retarded to a degree that they cannot understand the meaning and consequences of the operation.
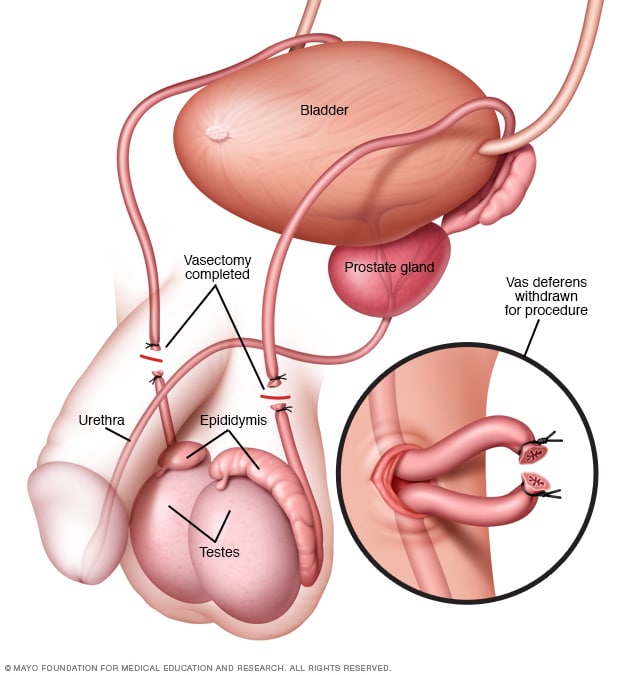
Vasectomy
This method is for the males who do not plan to have children any more. This is a simple surgical procedure that requires minor surgery of the tube that carries sperm to the ejaculatory duct. Vasectomy procedure prevents the sperm from entering the seminal fluid and thus prevents pregnancy. But the testis will continue the production of sperm which will be absorbed by the body itself. Hematoma formation and infection are the most complications.
 |
| Photo by Mayo Clinic |
Advantages
- It is permanent.
- It does not affect sexual performance.
- It is very simple and relatively safe to do.
- It increase sexual enjoyment since there is no need to be concerned about pregnancy.
Disadvantages
- It must done by a trained person.
- Uncomfortable for the first three (3) days.
- Swelling, bruising and pain in the scrotum.
- Infection of the incision site.
- The person feels faintness briefly after the operation.
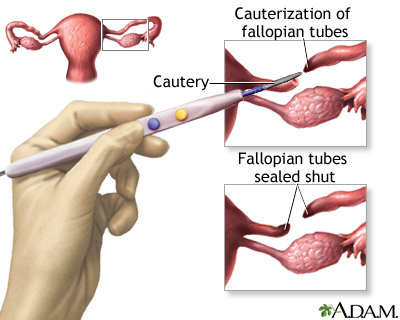
Female sterilization/Tubal ligation
 |
| Photo by MedlinePlus |
This method is also known as tubal sterilization which is a permanent contraceptive method for females. This again is a surgical procedure like vasectomy in males. The fallopian tubes that carry eggs from the ovaries to the uterus are blocked thus inhibiting pregnancy.
These are deep inside the peritoneal cavity, so their approach is a bigger procedure than operating on the male. The use of the laparoscope has reduced much of the need for large incisions in the majority of cases, but it is still an intraperitoneal operation requiring a general anaesthetic and the availability of full surgical skills.
Laparotomy sterilization
 |
| Photo by My Health Alberta |
The woman should plan to stay in hospital for 2-3 days depending on how fit she is. In the Irving method, each tube is divided and separated. The medial end is implanted in a tunnel in the wall of the uterus.
The operation of formal surgical division is commonly performed these days whilst doing an elective Caesarean section when the abdomen is open. The failure rate is about 2-4 per 1000 operations.
A lesser abdominal operation {Mini-Lap} often done in developing countries where laparoscopy is not readily available.. With this method, each fallopian tube in turn can be sought, drawn up through a 5cm transverse suprapubic incision and operated upon. It is divided and the two ends overlapped so that the ends are separated. The failure rate for this operation is about 1-2 per 1000 operations.
Advantages
- It has immediate protection against pregnancy.
- It does not interfere with sexual intercourse.
- It has no systemic effect.
- It is permanent.
- It is highly effective.
Disadvantages
- Chance of regret.
- Does not offer protection against STIs/HIV.
- It is not reversible.
- It can result in dispute among couple if education is not well done.
Emergency pills (post-coital contraception)
Oestrogen taken in large doses after unprotected coitus and before implantation may prevent pregnancy, Combined preparations containing 50mg of ethinyloestradiol and 250mg of levonorgestrei (Ovran or Norinyl-1) may be used in double dose. Two tablets are given immediately and repeated after 12 hours, High dose Ievonorgestrel alone is now the recommended emergency contraceptive.
The main side-effects are nausea and vomiting. Treatment should be given within 72 hours of single incident of unprotected intercourse. The woman should have a pregnancy test done if she does not menstruate.
Advantages
- It is easy to use.
- Doesn’t require consent from the male partner.
- Safe and effective in preventing pregnancy after unprotected sex.
- Available over-the-counter.
- It is the only contraceptive method which can be used when a woman forget her oral pill tablet.
- The only contraceptive which can be used when a condom burst during sexual intercourse.
Disadvantages
- It does not work if women are already pregnant.
- It has a limited time frame of 5 days following unprotected intercourse.
- Women still have a little chance of getting pregnant.
- No protection from sexually transmitted infections.
- May cause side effects like nausea (anti-nausea medication might help with this), vomiting, abdominal pain and headaches.
- Not as effective as some other types of birth control.
- Require a clinic visit and a prescription in some cases.
Counseling
Family planning and birth control need discussion of more than just the mechanics of the methods. They are a part of reproductive life linked with emotional and sexual life. There is sometimes embarrassment surrounding family planning and so this matter is not discussed openly.
It is for professionals to try and help break these barriers by discussing the matter in a clear and simple fashion. When discussing any method of contraception, consider;
- Suitability.
- Side-effects.
- Risks.
- Benefits.
- How it works.
- After sales services.
- Professional care needed.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts
Nanda Nursing Diagnosis 2021 - 2023 PDF
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments
Post a Comment