
Introduction
This is an acute and highly contagious lungs and intestinal
tract bacterial infection.
This is commonly spread from animals like cows, goats, and
sheep. The bacterial is a spore-forming bacterium which can live in the soil
and animal products for decades. This infection is potentially fatal.
Causative organism:
Bacillus Anthracis
Mode of transmission
- Through
direct contact with tissues of animals dying from the disease or direct contact
with contaminated hair, wool and soil. This causes cutaneous anthrax.
- Through
inhalation of spore of the organism causing pulmonary anthrax.
- Gastro-intestinal
anthrax: transmitted through eating contaminated meat from infected mammals especially
infected dead animals. This gastro-intestinal anthrax is difficult to recognize.
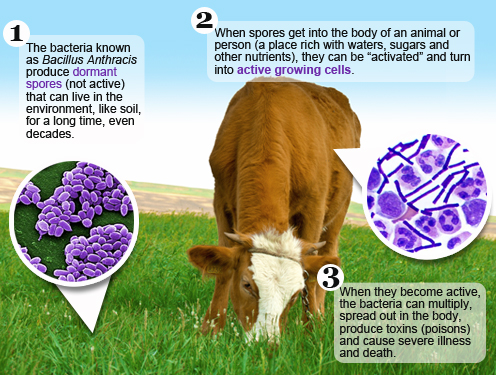 |
Photo by CDC
|
These categories of people are considered to be of high
risk;
- Veterinary
officers.
- Labouratory
Technicians.
- Employers
of textile Companies.
- Fulani
herds men.
Signs and Symptoms
- Itching of
the affected skin.
- Lesion
develops leading to black scab (eschar).
- Regional
lymphadenopathy.
- Oedema
around the slough.
- Pulmonary
anthrax: resemble common cold i.e. fever, headaches, cough etc.
- Acute
Symptoms of respiratory distress, shock and then death.
- Sudden and
general malaise.
- Septicaemia,
followed by death.
Management
- Penicillin injection
or oral tetracycline or erythromycin.
- Pulmonary
anthrax is treated with intravenous penicillin.
- Corticosteroids
e.g. dexamethasone may be given for skin itching or lung inflammation.
- If
treatment is delayed because diagnosis is not made promptly, death is likely.
Prevention and Control
- All
infected persons must be treated promptly and effectively.
- Proper
disposal of discharge from lesion or soiled articles.
- Prompt
isolation and treatment of animals suspected of anthrax.
- Consumption
of dead animals should be avoided.
- Vaccination
of all animals annually.
- Proper
cooking of meat before eating.
- All animals
should be examined before and after slaughtering and selling to the public.
- Proper
washing, disinfection of hair wool and hides before processing for sale.
- Health
education on cause, mode of transmission, signs and Symptoms as well as how to
prevent the disease.
- Notification
of the disease to the health authority.
Read Also

Comments
Post a Comment