Scroll down to proceed with verification👇🏾
Featured post
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
HIV/AIDS; mode of transmission, signs, diagnosis, management and prevention

Introduction
AIDS IS a syndrome characterized by opportunistic infections. It was first reported in 1981 in the USA and soon after, other countries started reporting cases. It was first reported in Ghana in 1986 and is now a pandemic disease. It is a sexually, as well as, blood-borne disease.
Causative organism: the Human Immune deficiency Virus (HIV) types 1 and 2. HIV is found in the body fluids such as semen, blood, vaginal secretions, cerebrospinal fluid and breast milk.
Incubation period: it can take between 2 and 10 years or more for signs to show. During this period, the person became a healthy carrier to infect others. When infected through blood transfusion it takes a shorter time to incubate.
Distribution: Worldwide, but some countries have more infections. There is no explanation as to why some countries have more infections than others. However, poverty, illiteracy, and high rate of other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), could be determining factors.
Susceptibility: general, but women and children are at risk. Since the transmission of HIV is predominantly heterosexual, women have a greater incidence of infection than men due to multiple reasons;
- During sexual intercourse, the semen from the man is deposited into the vagina together with the virus, the vaginal wall provides a wider surface for the entry of the virus.
- The vagina can easily have abrasions for easy entry of the virus
- Women with other STIs are often unaware of them for early treatment because, the signs are noticed at a later stage.
- Young girls are even at greater biological risk since their immature reproductive tract, renders it an ineffective barriers of HIV.
- Older women also become biologically more vulnerable after menopause.
- Young girls become sexually active earlier that their male counterparts and at a younger age, they lack the knowledge and power to control their sexually encounters.
- Financial dependence of women on men in developing countries, leave them with little or no control over how and when to have sex.
Mode of transmission
The common modes of transmission are;
- Direct sexual contact with infected persons through the vaginal, anal or oral routes. The most infectious mode being the anal route which usually results in rupture and abrasions of the anal mucosa through which the virus gets easy entry to the blood stream. The vaginal route, however, has the highest incidence in Ghana.
- Blood transfusion with infected blood.
- Incisions such as circumcision, scarification, tattooing and other surgical procedures with contaminated instruments and receiving treatment with piecing instruments like contaminated needles.
- Mother-to-child transmission; infected mother transmitting to the child during birth and through breastfeeding.
When the virus enters the body, it attacks and kills the helper ‘T’ lymphocytes which help in the immune system of the individual. The damaged ‘T’ cells are no longer able to stimulate the ‘B’ cells to produce antibodies that will attack and kill any invading organism in the body; the person is therefore left vulnerable to all kinds of infections.
When symptoms have not started, it is difficult to tell who is a carrier. At this Stage, the person is said to be HIV positive and not AIDS positive. When symptoms start, the person is said to have AIDS.
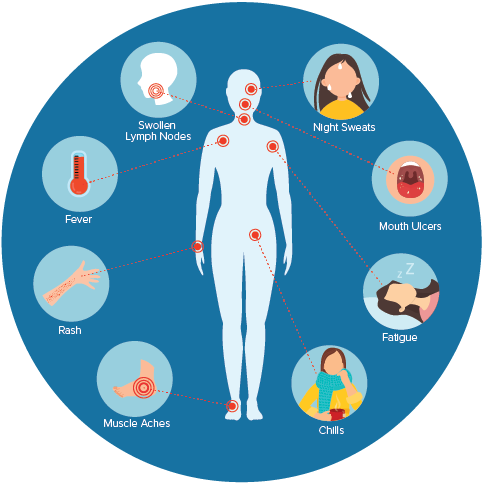
Signs and Symptoms
The major signs and symptoms include
- Prolonged fever lasting more than one month.
- Diarrhea persisting more than one month.
- Weight loss which is more than 10% of the original body weight.
Whereas the minor signs and symptoms
- Night sweats.
- Oro-pharyngeal thrush.
- Chronic cough for more than one month.
- Repeated attacks of herpes zoster.
- Generalized dermatitis.
- Kaposi’s sarcoma (a type of skin cancer).
- Multiple boils.
- Amenorrhoea in women without cause.
- Dementia.
- Persistent weakness.
- Pneumocysticcarinii (a type of pneumonia).
Diagnosis
A client having any two major signs and symptoms and any
other of the minor is confirmed as AIDs positive. However, the identification of an HIV/AIDS client with the signs and symptoms is
not always accurate. Suspected clients are confirmed with laboratory test.
There are a series of tests done to confirm an HIV positive status of a client with 3 different test kits. These are;
- First Response test kit
- Oraquick test kit
- SD Bioline
 |
| HIV test kits |
The algorithm for these tests differ a little between the general population and pregnant women. Below is the algorithm for each of these group of people.
 |
| HIV testing algorithm for non-pregnant women and general population. |
 |
| HIV testing algorithm for pregnant women |
We should note that infection with HIV/AIDs is shown by the presence of antibodies in the blood. However, these anti bodies do not protect the individual, and so the virus continues to multiply and remains in the person who becomes healthy carrier for a long period before signs and symptoms begin.
The white blood cells that the virus attacks and destroys are the CD4 cells. The strength of the body’s immune system is determined by CD4 test. The lower the count of the CD4 cells, the less immune you are. A normal count is between 600 and 800 microliter of blood.
The 'window period’ should be considered when conduction a laboratory test (e.g. ELISA). This is a period between the initial test and the repeated test after 6 months before confirming results. Thus, the result of the initial test can be negative while the repeated one becomes positive. One should therefore not assume a negative status after the initial test.
Management
There is no known cure for AIDS but there are drugs that slow down the virus from multiplying and therefore fewer viruses attack the immune system. These drugs are referred to as antiretroviral drugs (ART). The drugs also help the immune system to get stronger so that it can prevent opportunistic infections.
The use of ART means that client takes several different tablets every day and for ART to work, the client must take all the tablets at the same time every day.
The medicines for the ART are to be prescribed only by a doctor due to their side effects which are serious. They are therefore used where it is possible to monitor the client. These may include skin rashes, headache, nausea and diarrhea, pain in the hands and feet. Bad dreams, feeling tired, and kidney problems. It is necessary to always report side and adverse effects to your physician or doctor.
Some antiretroviral drugs commonly used in Ghana for ART include Zidovudine (AZT) or Retrovir (ZDV), Nevirapin(NVP), Stavudine, Delfmavir, Saquinavir, Delavirdine.
- Symptomatic management is given to infected persons.
- Apart from the management of HIV/AIDS. The family members must be involved in the care both in the home and in a health care facility.
- All care providers should understand and accept clients in their state in order for them to express their feelings and needs.
- Manage the opportunistic infection (syndromic management) early prevent complications.
- Confidentiality must be ensured to protect dignity of the client.
- Avoid being judgmental and ensure stigma reduction as much as possible in order to increase the acceptance level of client to increase their life span.
- Society should be made aware of the plight of affected persons in order for them to get the necessary support needed. They need love and financial support.
- Good nutritious diet; foods rich in fruits and vegetable is given to boost the immunity of client.
- Clients should be referred to the hospital when they become ill.
Schedule for prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT)
- Infected mother is give nevirapine at onset of labour.
- Baby is given nevirapine syrup within 72hrs after delivery.
- Anti-retroviral treatment for pregnant women starts at 28 weeks of gestation depending On CD4 count (CD4 count of 300 of less).
- Babies born of infected mothers who did not receive treatment is given treatment for 6 weeks.
Prevention and control
 |
| Photo from paho.org |
- The safest form of prevention is abstinence before marriage in order to reduce the chances of being infected.
- Encourage faithfulness between partners.
- Avoid unnecessary sexual exposure i.e. anal, oral and casual sex / Use condom for casual sexual intercourse if it cannot be avoided.
- Blood should be well screened before used for transfusion considering the window period.
- Infected mothers should be advised not to get pregnant to prevent infecting the child.
- Visit qualified institutions for health care to prevent contaminated articles being used for your treatment.
- Barbers, hair dressers, circumcisers and all others who use sharp and piecing articles must sterilize their instruments and articles before used on others.
- Education on the dangers of public enema, use of drugs where common enema syringes and needles are used.
- Increase awareness through health education via the media (including social media), churches, associations and school.
- Voluntary counseling and testing should be encouraged and the services made available and accessible for individuals to know their HIV status.
- Empower women to take control of their sexual lives to reduce the chances of getting infected.
- Activities of commercial sex workers should be monitored to prevent infecting their customers.
Sexually Transmitted Diseases
These are diseases that are transmitted through sexual intercourse. These diseases have become endemic because of increased prostitution and promiscuity particularly among the youth who are sexually active. Furthermore, factors such as, poverty and disregards for traditional norms result in early sexual exposure among the youth. This may be attributed to the increase in the incidence of STIs. Due to the sensitive nature of STI infections, most infected persons prefer visiting unqualified people or quack doctors for treatment resulting in inappropriate or under treatment.
There are several STIs, 5 of the most common ones include;
Read Also
General Nursing Management of Patients with Medical Pathology
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Popular Posts
Nanda Nursing Diagnosis 2021 - 2023 PDF
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment