Scroll down to proceed with verification👇🏾
Featured post
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
STIs; general knowledge, signs, management and prevention of gonorrhoea, syphilis, candidiasis.
These are diseases that are transmitted through sexual intercourse. These diseases have become endemic because of increased prostitution and promiscuity particularly among the youth who are sexually active. Furthermore, factors such as, poverty and disregards for traditional norms result in early sexual exposure among the youth. This may be attributed to the increase in the incidence of STIs.
Due to the sensitive nature of STI infections, most infected persons prefer visiting unqualified people or quack doctors for treatment resulting in inappropriate or under treatment.
There are several STIs, 5 of the most common ones include;
- HIV/AIDS
- Hepatitis B
- Gonorrhoea
- Syphilis
- Candidiasis
GONORRHOEA
Introduction
It is a sexually transmitted disease caused by a bacterium which infects both males and females. Gonorrhoea mostly affects the urethra, rectum or throat but can also affect the cervix in females.
Untreated gonorrhoea can cause serious and permanent health problems. In females, it can spread into the uterus or fallopian tubes and cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This disease was common among older men and women but the pattern has changed with increasing involvement of younger age groups in line with the changed sexual behavior pattern of this age group.
Causative organism: Neisseria gonorrhea
Incubation period: 2 to 5 days and sometimes as long as 2 weeks.
Mode of transmission
- Direct transmission through sexual intercourse with infected individuals. This involves vaginal, oral or anal sex.
- The eyes of babies get infected during delivery by infected mothers to cause ophthalmianeonatorum.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of gonorrhoea show earlier in males than in females. Below are the signs and symptoms of gonorrhoea.
Males
- Purulent discharge from the urethra within few days.
- The infection spreads to the epididymis of the testes.
- It may lead to urethral stricture (abnormal narrowing) due to scars left on the urethra.
Females
- About 80-90% of females are unaware of the infection.
- There is urethral or vaginal discharge.
- Inflammation of the fallopian tubes (salpingitis).
- Pelvic inflammation disease (PID).
Children with Ophthalmia neonatorum
- Redness and swelling of the conjunctivae.
- Discharge from the eye which is purulent.
- Oedema and redness of the eye lid.
Complications
- Septicemia.
- Meningitis.
- Infertility.
- Ectopic pregnancy due to adhesion from salpingitis.
- Blindness in children.
Management
Treatment of infected persons with:
- Tablets ciprofloxacin 500mg PO stat (do not give in pregnant women) or intramuscular ceftriaxone 250mg IM stat.
- Add capsules Doxycycline 100mg bid x 7/7.
Prevention and control
- Prompt and proper treatment of infected persons by qualified personnel.
- Identify, trace sexual contacts, and treat them.
- Avoid sexual intercourse when infected persons.
- Carefully dispose off discharges and freshly soiled articles.
- Encourage condom use if not sure of your partner’s status.
- Commercial sex workers should be encouraged to use condoms.
- Treat all pregnant women before they deliver.
- Wipe the eyes of newly born babies whose mother’s status is not known with normal saline.
- Routine testing for venereal diseases during the antenatal period should be intensified.
- Counseling of the sexually active persons on the mode of transmission and prevention, particularly on protected sex.
SYPHILIS
Introduction
It is a chronic relapsing bacterial infection which presents with skin lesions primarily, secondary stage affecting mucous membranes and tertiary stage involving bones, central nervous system and the cardiovascular system.
 |
| Photo by Nejm |
Causative organism: Treponemapallidum
Incubation period: 10 days to 10 weeks but commonly, 3 weeks.
Mode of transmission
- Direct sexual intercourse with infected persons.
- Perineal contact with semen, vaginal discharge and blood of infected persons.
- Perineal contact with freshly soiled articles of infected persons.
- It may also be transmitted through extra genital sites such as the mouth during kissing.
- Occasionally, it can be transmitted through blood transfusion.
Signs and Symptoms
Primary stage
- A lesion appears as a papule (small pimple) which is painless, developing at the site of infection.
- The papule forms pus and results in a painless sore called ‘chancer’ which heals spontaneously after a few weeks.
- There is enlargement of the local or regional lymph nodes.
 |
| Photo by Elseveier |
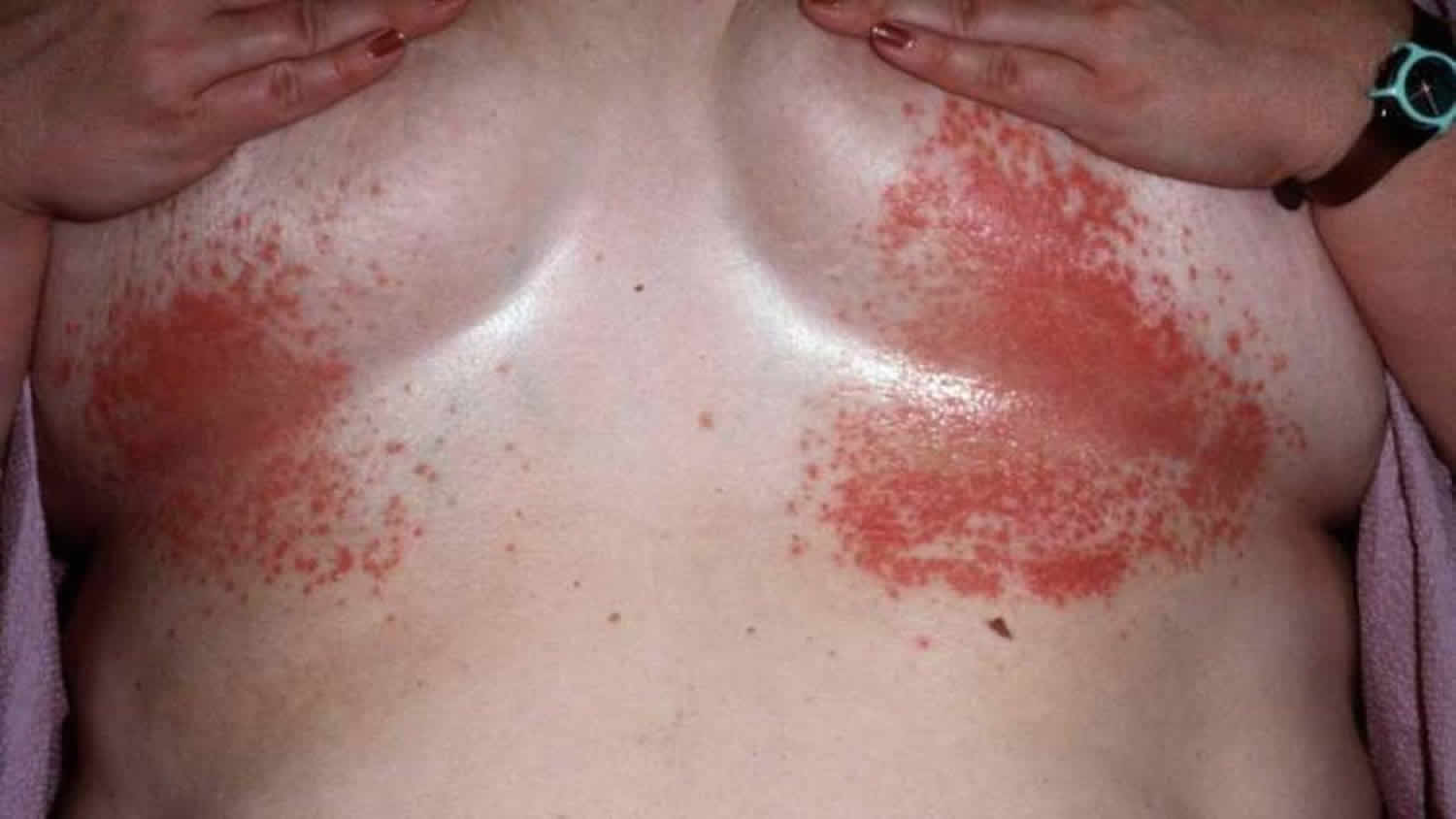
- The secondary lesions follow in about four months.
- There are mild systematic symptoms like fever and headaches.
- Generalized rashes which are painless but itchy.
- Generalized lymph node enlargements which are painless.
- These manifestation may disappear spontaneously.
 |
| Photo by The medifit |
- This phase is not infective but it is a phase of destruction and deformity.
- Osteomyelitis results due to weakness of bones.
- Narrowing of the aorta occurs, resulting in cardiac conditions.
- Pressure on the trachea and esophagus causing difficulty in swallowing.
- A destructive painless swelling appears on the body.
- Mental retardation may occur in children.
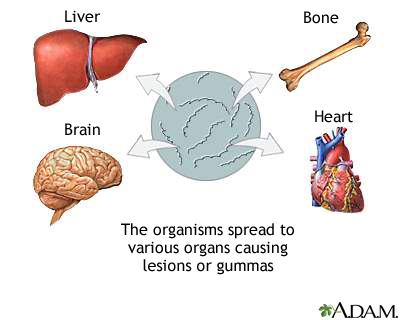 |
| Photo by medlineplus.gov |
Congenital Syphilis
When an infected mother gets pregnant, the foetus or unborn child may be born with the following;
- Saddle nose.
- Notched upper front teeth
- Deformity of the bones
- Bald patches in the head
- Blindness
- Mental retardation.
Management of syphilis
- Treatment of infected persons with Benzathine penicillin 2.4 MU IM stat. If penicillin allergic, give erythromycin or tetracycline.
- Ensure personal cleanliness.
- Adequate nutrition to boost the healing process.
- The chancre should be dressed to prevent flies and aid in healing.
Prevention and Control
- Effective treatment of all infected persons and their sexual partners.
- Provision of facilities for early detection, diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
- Control of commercial sex workers and promiscuous sexual behavior.
- Routine screening of pregnant women and blood donors and give treatment where necessary.
- Avoid contacts with discharges from open lesion and infected placenta.
- Use of condoms for casual sexual intercourse.
- Avoid kissing with infected persons and licking the genitals since it can be transmitted orally.
- Health education on the disease and its dangers.
CANDIDIASIS (Moniliasis)
Introduction
It is an infection caused by a yeastlike fungus that occur particularly in moist areas such as the mouth, vagina and skin folds. Some species of this fungus (Candida) normally lives inside the body and on the skin without causing problems. Candidiasis is classified as a sexually transmitted disease but is not usually spread by sexual contact.
 |
| Volvovaginal Candidiasis by teachmeobgyn.com |
 |
| Cutaneous Candidiasis by healthjade.net |
 |
| Candida Esophagitis by sciencephoto.com |
 |
| Oral Candidiasis by dentista-genova-dottpiccardo.it |
Causative organism: Candida albicans.
Incubation period: varies but in children, between 2-6 days.
Mode of transmission
- Direct transmission from the mucous surfaces of the mouth and vulva from which systemic spread may occur.
- Direct infection through broken skin.
- Indirect through freshly soiled articles of infected persons.
- Newborn babies are infected through the birth canal or from care givers hands.
Signs and Symptoms
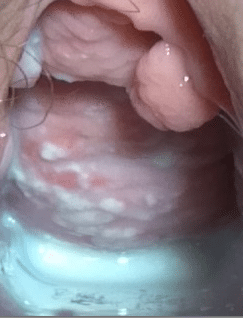
It depends on the site of infection, for genital candidiasis, the signs and symptoms include;
 |
| Photo by thecampusdoc.com |
- White or yellowish vaginal discharge.
- Irritation of the vagina and itching of the vulva area.
- White or grey raised patches on the vaginal wall with local inflammation.
- Painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia).
- Systemic infection produces fever and chills.
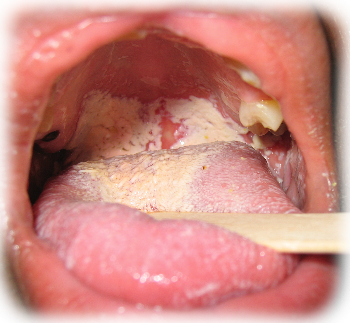
- In children, there is the oral thrush (cream-coloured patches on the tongue, mouth and pharynx).
Management
- Treatment with Miconazole vaginal tablets 200mg noct. x 3/7
- or Nystatin vaginal tablet and Tab Metronidazole 400mg bid x 7/7.
- Wash panties frequently and dry them in the sun.
- Wear airy and loose underwear’s to reduce moisture at the genital area.
- Regular washing of the vulva with clean water.
Prevention and Control
- Proper and adequate treatment of infected persons and their sexual partners.
- Practice safer sex by using condoms for casual sex.
- Treatment of infected pregnant women before they deliver, to prevent infecting babies in the process of childbearing.
Read Also
General Nursing Management of Patients with Medical Pathology
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Popular Posts
Nanda Nursing Diagnosis 2021 - 2023 PDF
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps


Really educative and very simple to understand
ReplyDelete