Featured post
Contents [ hide ] Introduction Actually, what you are experiencing is a normal physiological process that begins once a girl reaches puberty. The first menstruation in a woman’s life is referred to as menarche , this could happen between the ages of 10 to 15 with most (the average) girls having theirs around age 12. It involves bleeding from the uterus at regular intervals. The end of menstruation is termed menopause , this usually happens between the ages of 45 to 55. Menstruation is therefore defined as the cyclical or monthly flow of blood and shedding of endometrium including mucus, some enzymes and unfertilized ovum. So, what really happens? Well in simple terms, it all begins with changes in hormones in the body. You can think of hormones as messengers that are sent by some organs of your body to tell other cells to do something. In this particular case, an organ called hypothalamus which is found in your brain begins the process. [Fast forward] The ovaries release f...
Hepatitis B (Serum Hep.): signs and symptoms, mode of transmission, management and prevention

Introduction
It is a sexually transmitted, as well as blood-borne disease
caused by a DNA virus. The virus is known as hepadnavirus and can cause both acute and chronic forms of
hepatitis.
Causative organism:
Hepatitis B virus.
Incubation period:
between 45 and 180 days.
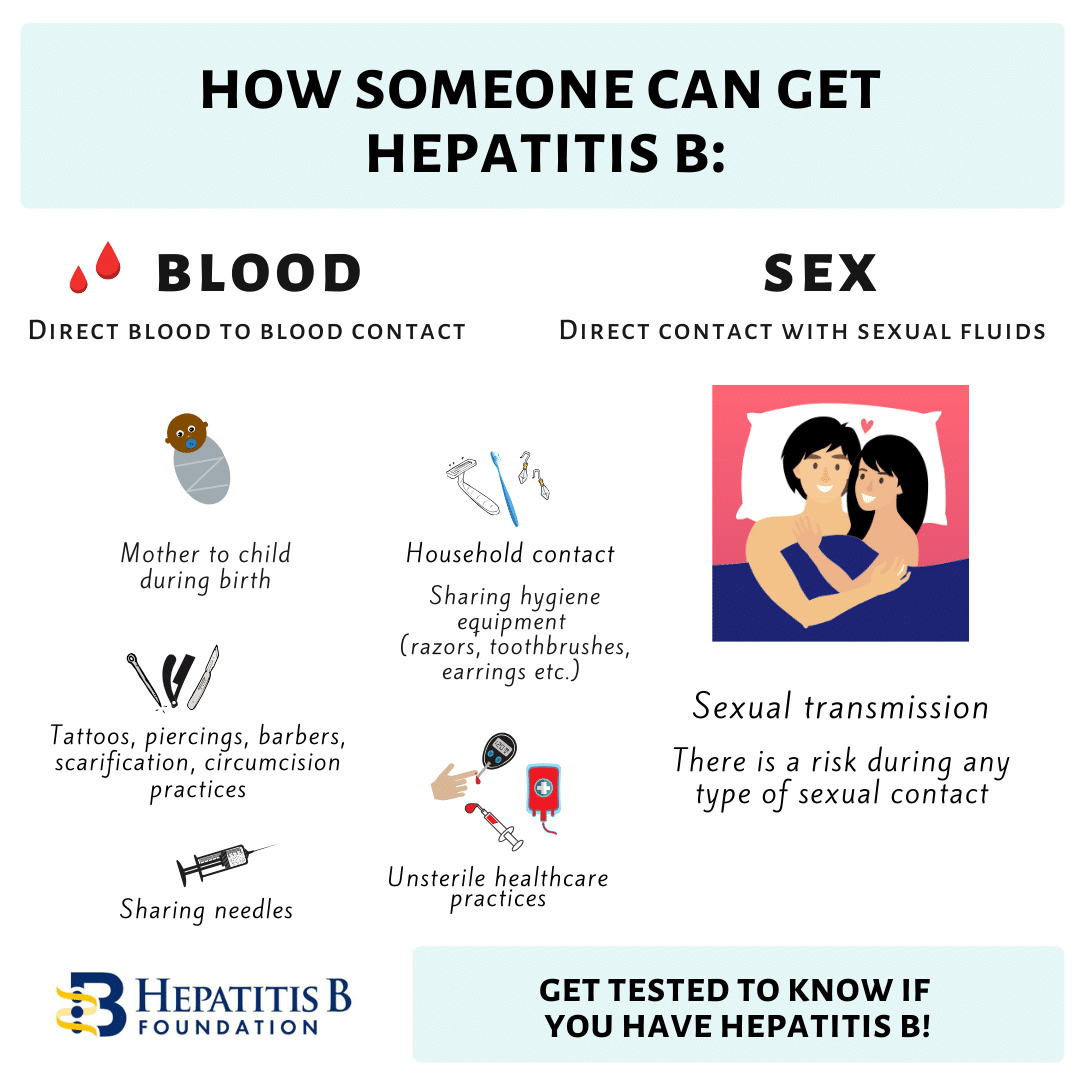
Mode of transmission
- Injection given with needles contaminated by body fluids
of infected persons or carriers.
- Sexual intercourse with infected person.
- Kissing with infected persons may spread it since the virus
is present in saliva.
- Transfusion with infected blood.
- Carrier mothers can transmit to their new born during the
birth process.
- Indirectly from exudates from the skin ulcers of infected
persons.
- Sweat and tears of infected persons have also been found
to contain the virus.
Signs and Symptoms
- Prodromal period of headache, malaise, nausea, anorexia
and fever for 2-14 days.
- Followed by vomiting and pain in the right hypochondria.
- Jaundice appears with variable severity after prodromal
symptoms subside.
- Dark urine and pale stools.
- In most cases patient may recover completely, but there
may be relapse.
- Clinically it may be difficult to distinguish between the
signs and symptoms of hepatitis A and B.
Management
- There is no known treatment. Treatment is symptomatic
since it is caused by a virus.
- Care providers should understand the clients, avoid being
judgmental (most people attribute it to promiscuity) and give assurance of good
care to them.
- Ensure enough rest.
- Give plenty of fluid especially glucose drinks, fruit
drinks, water, rice water.
- Give a lot of vitamin rich foods.
Prevention and control
- Encourage abstinence until marriage and partners should be
faithfully to each other to reduce the risk of being infected.
- Avoid unnecessary' casual sex exposure.
- Use condom for casual sexual intercourse if it cannot be
avoided.
- Visit qualified institutions for health care to prevent
contaminated articles being used for your treatment.
- Sharp and piercing instruments should be sterilized after
use.
- Blood should be well screened before transfusion.
- All children should be given active immunization against
the disease with DPT/HibHepB vaccine.
- Care providers and health care workers at risk should be
give Hepatitis B vaccine.
- People who get exposed to the virus should be given
passive immunity with hepatitis B immune vaccine.
- Some persons become life-long carriers and so must be
educated to prevent infecting others.
Read Also

I was diagnosed as HEPATITIS B carrier in 2013 with fibrosis of the
ReplyDeleteliver already present. I started on antiviral medications which
reduced the viral load initially. After a couple of years the virus
became resistant. I started on HEPATITIS B Herbal treatment from
ULTIMATE LIFE CLINIC (www.ultimatelifeclinic.com) in March, 2020. Their
treatment totally reversed the virus. I did another blood test after
the 6 months long treatment and tested negative to the virus. Amazing
treatment! This treatment is a breakthrough for all HBV carriers.