Introduction
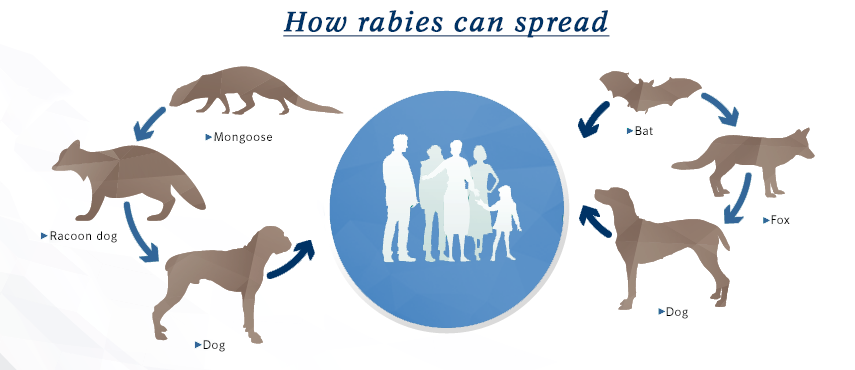
This is an acute notifiable and deadly communicable disease transmitted by a bite from an infected animal caused by rhabdovirus which is found in the saliva of infected animals (usually dogs, cats, foxes. wolves and bats).
Mode of transmission: this is by the bite of an infected mammal, most commonly stray (and also cats, wolves, and bats).
 |
| Photo by Boehringer Ingelheim |
Incubation period: 9 - 90days.
Diagnosis: history of dog or bat bite plus neurological features
Clinical feature
- Prodromal symptoms;
- Itching and pain at the site of bite.
- Fever.
- Chills.
- Malaise.
- Headache.
- Hydrophobia.
- Involuntary movement and muscle spasms.
- Hallucinations.
- Very aggressive.
- Paraplegia and loss of sphincter control.
- Intense excitement.
Treatment
- Observe the biting animal if possible to see if the animal dies.
- Clean the wound.
- Give tissue-culture rabies vaccine on 0, 3, 7, 14, 30 and 90 days.
- Give anti-tetanus toxoid.
- Give rabies immune globulin (RIG) if possible (give around the wound). Discontinue treatment if the dog/mammal remains healthy for 10days.
- The patient should be sedated with diazepam if there is agitation and supplemented by chlorpromazine 50-lOOmg if necessary.
Prevention
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis with human diploid cell strain vaccine.
- Post-exposure prophylaxis with human rabies immunoglobulin.
Read Also










0 Comments